PON technology, GPON, XG(S)-PON, EPON and 10G-EPON, is widely used in optical access network, such as Huawei ZTE Nokia and Fiberhome OLT ONT/ONU. This article will introduce PON, and compare GPON, XG(S)-PON, EPON and 10G-EPON different features.
What Is GPON?
Passive Optical Network (PON) is a point to multi-point (P2MP) passive optical network. Mainstream PON technologies include broadband passive optical network (BPON), Ethernet passive optical network (EPON), and gigabit passive optical network (GPON). Adopting the ATM encapsulation mode, BPON is mainly used for carrying ATM services. With the obsolescence of the ATM technology, BPON also drops out. EPON is an Ethernet passive optical network technology. GPON is a gigabit passive optical network technology and is to date the most widely used mainstream optical access technology. GPON is defined by ITU-T Recommendation G.984.x. Figure 1 shows a GPON network architecture.
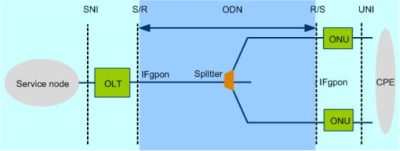
Figure 1 GPON network architecture
| IFgpon: GPON interface | SNI: Service Node Interface |
| UNI: User to Network Interface | CPE: Customer Premises Equipment |
What Is XG(S)-PON?
XG(S)-PON is evolved from the existing GPON technology, the factors promoting the technology evolution to XG(S)-PON are as follows:
- Developing services require higher bandwidths and the GPON technology cannot meet bandwidth requirements.
- Innovative access technologies on the user side require higher bandwidths and the GPON technology will face bandwidth bottlenecks.
- A greater split ratio and a longer transmission distance increase network construction investments.
What is EPON?
The EPON network uses two wavelengths of a single fiber to transmit bidirectional 1.25Gbit/s digital signals. The uplink direction uses a 1310nm wavelength window, and the downlink direction uses a 1490nm wavelength window. The EPON network is composed of OLT (Optical Line Terminal), ONU (Optical Network Unit) and ODN (Optical Distribution Network). The physical topology is a point-to-multi-point tree network, and the logical topology is multiple point-to-point links from the OLT to each ONU. . Among them, ODN plays the role of connecting OLT and ONU.
What is 10G-EPON?
10G-EPON is an enhanced next-generation EPON technology evolved on the existing EPON technical standard, which mainly solves the following problems of EPON network:
- The continuous development of high-bandwidth business types has higher requirements for bandwidth, and EPON technology cannot provide enough bandwidth to meet the demand.
- The user-side access technology continues to innovate, and the user access bandwidth continues to increase. EPON technology will become a bandwidth bottleneck.
- The splitting ratio and transmission distance directly affect the investment in network construction.
10G-EPON is the same as the EPON network structure and follows the P2MP architecture of the standard PON network
GPON, XG(S)-PON, EPON and 10G-EPON functions and features comparison
| Specifications | EPON | 10G EPON | GPON | 10G GPON |
| Operating Wavelength | Tx:1490nm Rx:1310nm |
1G channel: Tx:1490nm Rx:1310nm 10G channel: Tx:1577nm Rx:1270nm |
Tx: 1490 nm Rx: 1310 nm |
Tx: 1577nm Rx: 1270nm |
| Bandwidth | Tx: 1.25 Gbit/s Rx: 1.25 Gbit/s |
Tx: 10.3125 Gbit/s Rx (asymmetric rates): 1.25 Gbit/s Rx (symmetric rates): 10.3125 Gbit/s |
Tx: 2.488 Gbit/s Rx: 1.244 Gbit/s |
Tx: 9.953Gbit/s Rx (asymmetric rates):2.488Gbit/s Rx (symmetric rates): 9.953 |
| Split ratio | 1:64; | 1:128 | B+: 1:64 C+/C++: 1:128 |
1:256 |
| T-CONTs per PON port | / | / | 1024 | 2048 |
| GEM ports per PON port | / | / | 3872 | 4096 |
| DBA | Minimum allocation granularity: 64 kbit/s Minimum allocated bandwidth: 256 kbit/s |
Minimum allocation granularity: 640 kbit/s Minimum allocated bandwidth: 2.5 Mbit/s |
Minimum allocation granularity: 64 kbit/s Minimum allocated bandwidth: 1 Mbit/s |
Minimum allocation granularity: 256 kbit/s Minimum allocated bandwidth: 1 Mbit/s |
| FEC | FEC is disabled by default | Symmetric rates, FEC is enabled in the upstream direction; Asymmetric rates, FEC is disabled in the upstream direction by default. |
FEC is disabled by default | FEC is enabled in the downstream direction and disabled in the upstream direction by default. |
| TDM bearing | CESOP | CESOP | CESOP TDM over ETH |
CESOP |
| Fiber length | Maximum logical reach: 40 km Maximum differential reach: 40 km |
Maximum logical reach: 60 km Maximum differential reach: 60 km |
Maximum logical reach: 60 km Maximum differential reach: 20 km |
Maximum logical reach: 100 km Maximum differential reach: 40 km |
| ODN protection | Type B; Type C; Type x dual-homing | Type B | Type B; Type C; Type x dual-homing | Type B |
| Packet encryption | Triple churning encryption or downstream encryption | Triple churning encryption or downstream encryption | Downstream: AES-128 | Downstream: AES-128 (See note 2.) |
| Authentication mode | MAC; LOID | MAC; LOID | SN; Password; 10 bytes; LOID | SN; Password; 10 bytes; LOID |
| Max receiving sensitivity | PX20: -27dBm PX20+:-30dBm PX20++: -34dBm |
PRX30(asymmetric): -29.78dBm PR30+ (symmetric): 10G channel: -29dBm 1G chanel: -33dBm |
Class B+: -28dBm Class C+: -32dBm Class C++: -35dBm |
N1: -27.5dBm N2a: -29.5dBm N2: -28dBm/-29.5dBm |
| Optical module parameters | Temperature, bias current, voltage, Tx optical power, Rx optical power | |||