With the rapid development of optical telecommunication, “Fiber replaces copper” already occurred in most countries, that means coaxial-cable or Ethernet cable were totally replaced by fiber. While optical transceiver is one of the core components of the fiber communication. If you do not know much about Data communication optical SFP transceiver (transceivers of switch, router, GPON OLT uplink and so on), this article is helpful for you to know it.
Structure of Optical Transceiver
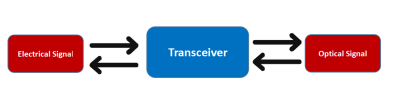
Exactly speaking, optical Transceiver/module, is a general name of various modules, includes Transmitter, Receiver, Transceiver (optical transmitter and receiver) and Transponder. But nowadays, optical transceiver stands for all these parts. Transceiver works at physical layer, the bottom of OSI model, performs Electrical and Optical signal conversion.
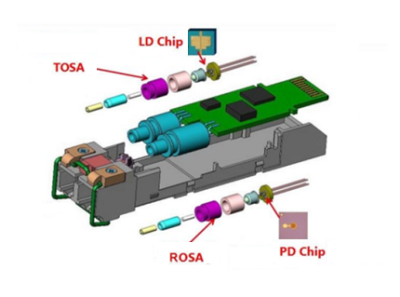
Components of an optical transceiver:
- Transmitting device (TOSA, optical laser)
- Optical receiving device (ROSA, including optical detector),
- Functional circuit
- Optical (electrical) interface
Structure Diagram
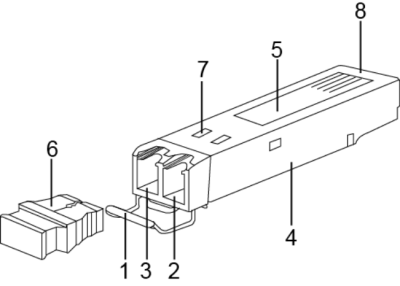
- Handle 2. Receiver 3. Transmitter
- Shell 5. Label 6. Dust cap
- Spring 8. Module connector
At the transmitting end, the driver chip processes the original electrical signal, and then drives the semiconductor laser (LD) or light-emitting diode (LED) to emit modulated optical signals.
At the receiving end, light detection diode converts optical signal to electrical signals, After going through a pre-amplifier, there outputs electrical signal.
Five main factors of Optical Transceiver
1, Encapsulation mode
2, Rate
Encapsulation mode is the most important way to distinguish optical transceivers, usual encapsulation modes are GBIC, SFP, eSFP, SFP+, XFP, SFP28, QSFP, QSFP28, CFP, CFP2, QSFP-DD etc., encapsulation mode is relative to rate.
Below is the development course of transceiver, and corresponding transmission rate.
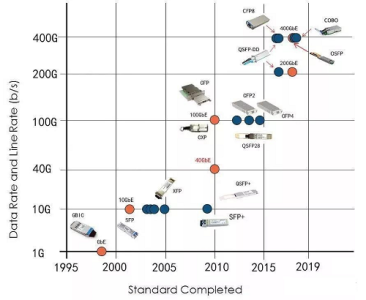
GBIC, 1000M
GBIC, Giga Bitrate Interface Converter (1000M rate), before 2000, GBIC was the most popular optical module Encapsulation mode and the most widely used gigabit module form.

SFP/eSFP, 1000M
SFP or eSFP, small Form-factor pluggable, half smaller size than GBIC, save more interface space, also 1000M rate, so GBIC is replaced when SFP comes out.
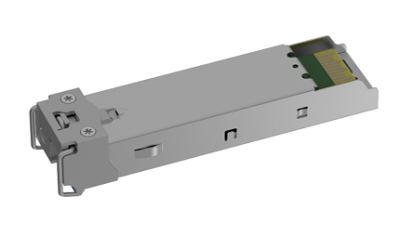
XFP, 10G
10-Gigabit Small Form-factor Pluggable, 10G rate.

SFP+, 10G
Also same rate as XFP 10G, but more compact than XFP (about 30% smaller), lower power consumption.
Huawei and 10G SFP+ modules for example are OMXD30000 02318169 850nm 10GE 0.3km LC Transceiver Module, OSX010000 02318170 1310nm 10GE 10km LC Transceiver Module.

SFP28, 25G
Same size as SFP and SFP+, to some extend, 25G SFP28 is a compromise solution for high price period of 40G and 100G, but even now, some Huawei switch models have 25 ports, and some ISPs have requirement for 25G rate.
Huawei and Cisco 25G module for example, Huawei SFP-25G-LR 02312LSE 25G 10km LC Transceiver Module, Cisco SFP-10/25G-CSR-S 850nm 10/25GBASE-CSR SFP28 Transceiver Module
QSFP/QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP28-DD, 40G/100G/200G
Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable, 4-channel SFP ports.
QSFP can be divided into 4*10G QSFP+, 4*25G QSFP28, 8*25G QSFP28-DD
Taking QSFP28 as an example, suitable for 4*25G interface, it can across over 40G and upgrade from 25G to 100G directly, wiring simplified significantly and costing reduced largely.
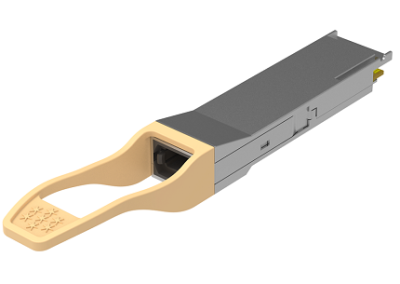
QSFP-DD, published in Mar. 2016, DD refers to “Double Density”. It adds 4 channels based on QSFP 4 channels, total 8 channels, and compatible with the QSFP solution.
Each channel of QSFP-DD adopts 25Gbps NRZ or 50Gbps PAM4 signal format. It supports up to 400Gbps rate under PAM4 format.
Fo example Cisco QSFP-100G-CWDM4-S 1310nm 100GBASE CWDM4 QSFP Transceiver Module, Huawei QSFP-100G-CWDM4 02311MNN 100G 2km LC Transceiver Module
Remarks:
PAM4 (4 Pulse Amplitude Modulation) and NRZ (Non-Return-to-Zero) are “Doubling” technology
For transceivers, if rate needs to be increased the, either increasing channels quantity or increasing per channel rate.
CFP/CFP2/CFP4/CFP8, 100~400G
Centum gigabits Form Pluggable, rate can reach to 100~400G.
CFP is larger size than SFP, supports single 100G channel, or multi 40G channels.

CFP is 2-time size of CFP2 and CFP8, 4-time size of CFP4
CFP is the specific encapsulation mode of 400G, supports 25Gbps and 50Gbps, realizes 400Gbps through 16*25G or 8*40G electrical interface. 400G transceiver price is very high, since it is not commercial used in large scale.

3, Mode
SM, Single mode; MM, multi-mode
SM transceiver is suitable for long-distance transmission, while MM module is for short-distance.
Differences:
| Items | Single mode | Multi-mode |
| Wavelength | 1310nm, 1550nm | 850nm |
| Distance | Long distance
10, 40, 80, 120km |
Short-distance
0.1, 0.3, 0.5km |
| Optical Fiber Type (diameter) | 9/125μm | 50/125μm or 62.5/125μm |
| Optical source | LD or LED with narrow spectral line | light-emitting diode or laser |
| Applications | lines with high rates and long distances (metropolitan network construction) | Lines in short-distance transmission, and transmission with many network nodes and connectors |
| Price | Expensive | Cheap |
4, Wavelength
Most common wavelength is 850nm, 1310nm, 1490nm, 1270nm 1550nm
5, Transmission distance
0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 10, 40 80km 120km for even longer distance.
Actually these five factors are inter-related, Short distance 0.1km 0.3km 0.5km=MM=850nm, long distance 10km 40km=SM=1310 1550nm
Basic Index of Optical Transceiver
| Index | Definition |
| Output optical power | The output optical power of optical source at the transmitting end of the optical module |
| Max Sensitivity | The minimum received optical power of the optical module under condition of a certain rate and bit error rate, unit: dBm. |
| Extinction Ratio | The minimum ratio value of the average optical power of the signal to the average optical power of the space sign under the condition of full modulation |
| Optical saturation | The Max input optical power when maintaining a certain bit error rate (10-10 to 10-12) at a certain transmission rate, unit: dBm |
Other Special optical transceiver
DWDM CWDM Module
WDM, Wavelength Division Multiplexing, it multiplexes different wavelength optical signal into one fiber to transmission. DWDM, is Dense WDM; CWDM, is Coarse WDM.
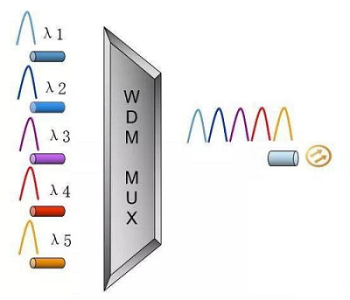
| Type | Full Name | Wavelength | Wavelength Interval |
| CWDM | Coarse WDM | 1270~1610nm | 20nm |
| DWDM | Dense WDM | 1528~1623nm | 0.8/0.4nm |
The advantage of WDM modules is long-distance transmission.
BIDI Module
BIDI(Bi-directional), it means Single Fiber Dual Directions. BIDI module is a module using WDM bidirectional transmission technology, which realizes bidirectional transmission in the optical channel on one optical fiber at the same time.
Dual fiber bidirectional module, one fiber transmit and the other receive.
BIDI module vs Dual fiber bidirectional module
1, BIDI module uses WDM technology, dual fiber module does not.
2, BIDI module works in pairs, dual fiber module does not.
4, BIDI module structure is more compatible than dual fiber module, and it has optical splitter and combiner.
5, Among BIDI modules, only one fiber is needed; dual fiber modules need two pieces fiber.
BIDI module is expensive then normal module, but the most obvious advantage is the cost of fiber infrastructure reduced.
Data communication optical transceiver is hot-product in the market, due to 5G and data center have large demands for it; above are the basic aspects about transceiver, if you have some comments or requirements for transceivers, welcome to contact fiberolt.com.





















